Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Abdominal Ultrasound
Test Overview
An abdominal ultrasound takes pictures of the organs and other structures in your upper belly. It uses sound waves to show images on a screen.
Areas that can be checked include the:
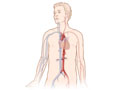
- Abdominal aorta. This large blood vessel passes down the back of the chest and belly. It supplies blood to the lower part of the body and the legs.
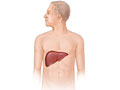
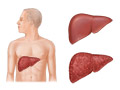
- Liver. This large organ lies under the rib cage on the right side of the belly. It makes bile (a substance that helps digest fat). It also stores sugars and breaks down many of the body's waste products.
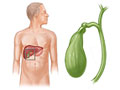
- Gallbladder. This small organ is right under the liver. It stores bile. When you eat, the gallbladder contracts to send bile to the bowels (intestines). The bile helps your body digest food and absorb vitamins that dissolve in fat.
- Spleen. This organ helps fight infection. It also filters old red blood cells. The spleen sits to the left of the stomach, just behind the lower left ribs.
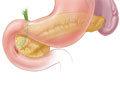
- Pancreas. This gland is in the upper belly. It makes enzymes that help digest food. The digestive enzymes then move into the bowels. The pancreas also releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin helps the body use sugars for energy.
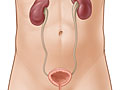
- Kidneys. This pair of organs is in the upper part of your belly, but toward your back. The kidneys remove wastes from the blood. They also make urine.
If your doctor needs more details about a specific organ in the upper part of your belly, you may get a special ultrasound, such as a kidney ultrasound. If you need the structures and organs in your lower belly checked, you will get a pelvic ultrasound.
Why It Is Done
Abdominal ultrasound is done to:
- Find the cause of belly pain.
- Find, measure, or monitor an aneurysm in the aorta. An aneurysm may cause a large, pulsing lump in the belly.
- Check the size, shape, and position of the liver. It may also check for problems of the liver. These include jaundice, cirrhosis, or fatty liver. This test may be done to follow up after liver function tests.
- Look for gallstones, inflammation of the gallbladder, or blocked bile ducts.
- Learn the size of an enlarged spleen and look for damage or disease.
- Find problems with the pancreas, such as a tumor.
- Look for blocked urine flow in a kidney. If needed, a kidney ultrasound can find out the size of the kidneys, detect a mass, or detect fluid surrounding the kidneys. It can also look for causes of bladder infections that won't go away. Or it can check how the kidneys are doing after a transplant.
- Find out if a mass in a belly organ is a solid tumor or a fluid-filled cyst.
- Guide the placement of a needle or other tool during a biopsy.
- Look for fluid buildup in the belly cavity. This problem is called ascites. An ultrasound also may be done to guide the needle during a paracentesis. This is a procedure to remove fluid from the belly cavity.
How To Prepare
What you need to do depends on the reason for the ultrasound. For example:
- If you are having your liver, gallbladder, spleen, and pancreas checked, you may need to eat a fat-free meal on the evening before the test. Then you may need to avoid eating for 8 to 12 hours before the test.
- For a test of the kidneys, you may be asked to drink 4 to 6 glasses of liquid about an hour before the test. This is to fill your bladder. You may need to avoid eating for 8 to 12 hours before the test to avoid gas buildup in the intestines. Gas could affect the results of the kidney ultrasound.
- If you are having your aorta checked, you may need to avoid eating for 8 to 12 hours before the test.
How It Is Done
Before the test
- You need to remove any jewelry that might get in the way of the test.
- You need to remove all or most clothing around the area to be scanned. You get a cloth or paper covering to use during the test.
During the test
- You lie down on an exam table.
- The doctor or technologist spreads some warm gel on your belly to improve the transmission of the sound waves. A small handheld unit called a transducer is pressed against your belly and is moved back and forth. A picture of the organs and blood vessels can be seen on a video monitor.
- You need to lie still. You may be asked to take a breath and hold it for several seconds during the scanning.
- You may be asked to change positions during the test so more scans can be done.
How long the test takes
The test will take about 30 minutes. You may be asked to wait until the radiologist has reviewed the scan. The radiologist may want to do more ultrasound views of some areas of your belly.
How It Feels
Most people do not feel pain during the test. If your belly hurts already from an injury or illness, the slight pressure from the transducer may be somewhat painful. You will not hear or feel the sound waves.
Risks
There are no known risks from having this test.
Results
Normal:
- The organs have a normal size, shape, and texture. No abnormal growths are seen. No fluid is in the belly.
- The aorta looks normal. No aneurysms are seen.
- The thickness of the gallbladder wall is normal. The size of the bile ducts is normal. No gallstones are seen.
- No kidney stones are seen. The system that drains the kidneys is not blocked.
Abnormal:
- An organ looks abnormal. It may be smaller than normal. A growth may press against it or may be seen in an organ. Or fluid may be seen in the belly cavity. These things may be due to inflammation, infection, or other diseases.
- The aorta is enlarged or an aneurysm is seen.
- The liver looks abnormal. This may point to liver disease (such as cirrhosis or cancer).
- The walls of the gallbladder are thickened, or fluid is found around the gallbladder. These may point to inflammation. The bile ducts may be enlarged. Or gallstones may be seen.
- The kidneys or the ureters are enlarged because urine does not drain as it should. Kidney stones are seen. (But not all stones can be seen with ultrasound.)
- An area of infection or a fluid-filled cyst is seen inside an organ. Or the spleen may be ruptured.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: March 26, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: March 26, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2026 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.